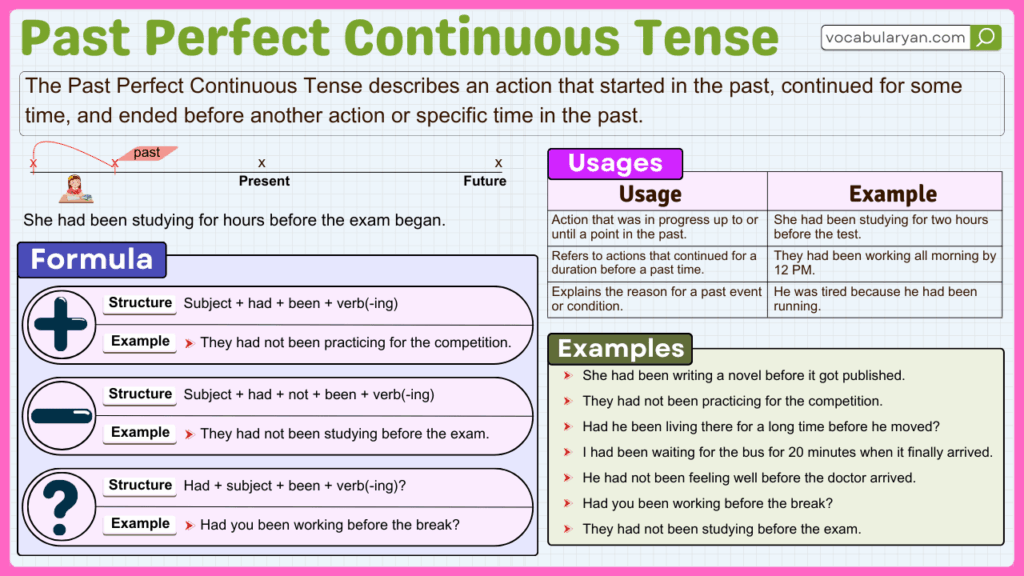
Learning the Past Perfect Continuous tense is important for expressing actions that started in the past and continued up to another past moment. It is formed using had been + verb + -ing, as in “She had been studying for hours before the exam” or “They had been waiting when the bus finally arrived.” This tense helps show the duration and continuity of past activities. Mastering the Past Perfect Continuous tense improves your ability to describe complex past events with clarity and detail.
Structures of the Tense
Affirmative:
Subject + had been + verb(ing) + object + time expression
- She had been studying before her friend arrived.
- They had been working for five years when it shut down.
Negative:
Subject + had not been + verb(ing) + object + time expression
- He had not been sleeping before the doctor prescribed medicine.
- We had not been waiting long when the bus arrived.
Interrogative:
Had + subject + been + verb(ing) + object + time expression?
- Had she been practicing before the performance?
- Had they been living there for ten years?
Double Interrogative:
Question word + had + subject + been + verb(ing) + object + time expression?
- Why had she been crying before the meeting?
- How long had you been working before you resigned?
Subject-Verb Agreement
Subject-verb agreement ensures that the helping verb and main verb correctly match the subject. Here is a table to help you understand how different subjects use past perfect continuous tense.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Main Verb (ing form) |
|---|---|---|
| I | had been | working |
| He | had been | studying |
| She | had been | reading |
| It | had been | running |
| You | had been | waiting |
| We | had been | planning |
| They | had been | traveling |
| The teacher | had been | teaching |
| My father | had been | fixing |
| Dogs | had been | barking |
Time Expressions
Time expressions are essential in past perfect continuous tense because they indicate the duration or point in time when the action was happening before another event.
For:
- She had been studying for three hours.
Since:
- They had been living there since 2010.
Before:
- He had been practicing before the match.
Until:
- She had been working until midnight.
By the time:
- By the time we arrived, they had been waiting.
All day:
- He had been feeling sick all day.
All night:
- She had been crying all night before the flight.
The whole week:
- They had been traveling the whole week.
For a long time:
- We had been planning the trip for a long time.
For months:
- He had been training for months before the competition.
Adverb Placement in Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Adverbs should be placed correctly in a sentence to maintain clarity and proper meaning. In this tense, adverbs usually go between had been and the main verb.
- She had been carefully writing before the deadline.
- He had been constantly practicing before the competition.
- They had been quietly studying before the test.
- We had been seriously considering a move before the job offer.
- She had been patiently waiting for the bus.
- He had been regularly exercising before the race.
- They had been slowly improving their skills.
- We had been frequently calling before the meeting.
Uses of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense is used in different situations, from describing ongoing actions before a past event to explaining the reason behind a past situation.
Duration before another event:
- She had been working for five years before she resigned.
Cause and effect:
- He was exhausted because he had been running.
Past habits over a period:
- They had been meeting every weekend.
Interrupted actions:
- I had been reading when the phone rang.
Repeated actions:
- He had been calling her every day.
Background descriptions:
- It had been raining for hours before the sun came out.
Showing dissatisfaction:
- She had been waiting for too long.
Actions affecting emotions:
- She was angry because they had been lying to her.
Short Answers
| Question | Short Answer |
| Had she been working late? | Yes, she had. / No, she hadn’t. |
| Had they been studying? | Yes, they had. / No, they hadn’t. |
| Had the dog been barking? | Yes, it had. / No, it hadn’t. |
| Had we been waiting long? | Yes, we had. / No, we hadn’t. |
| Had he been playing football? | Yes, he had. / No, he hadn’t. |
| Had you been feeling unwell? | Yes, I had. / No, I hadn’t. |
Question Tags
| Statement | Question Tag |
| She had been reading, | hadn’t she? |
| They had been working, | hadn’t they? |
| The children had been playing, | hadn’t they? |
| He had been waiting, | hadn’t he? |
| We had been talking, | hadn’t we? |
| You had been helping, | hadn’t you? |
Examples of Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Seeing examples in different forms helps understand how this tense is used. Below are various examples of past perfect continuous tense in affirmative, negative, and interrogative sentences.
- They had been studying before the exam.
- I had been working before I presented it.
- He had been reading before he lost it.
- She had not been sleeping well before vacation.
- They had not been exercising before the gym.
- We had not been talking before the reunion.
- Had she been working before she quit?
- Had I been learning French before moving?
- Had we been eating before they arrived?
Common Mistakes with Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Learners often make errors while using the Past Perfect Continuous Tense. Here are some common mistakes along with their correct forms.
- He had been works in the office for five years ❌
He had been working in the office for five years ✅ - They had been went to school before it rained ❌
They had been going to school before it rained ✅ - Had she been studies before the test? ❌
Had she been studying before the test? ✅ - She had not been cooks before learning recipes ❌
She had not been cooking before learning recipes ✅
FAQ’s about Past Perfect Continuous Tense
What is the difference between Past Perfect and Past Perfect Continuous?
The Past Perfect focuses on completed actions, while the Past Perfect Continuous emphasizes duration.
Which time expressions are commonly used with this tense?
For
Since
Before
Until
By the time
All day
All night
The whole weekWhat is the difference between had been doing and was doing?
Had been doing refers to an action continuing before another past event, while was doing
refers to an action happening at a specific moment in the past.Can I use this tense without mentioning a specific duration?
Usually, a time expression is needed, but in some contexts, it can be omitted if the duration is implied.
You May Also Like
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
