English is a language filled with words that sound similar but have completely different meanings. Understanding these commonly confused words can significantly improve your communication skills, both in writing and speaking. Below is a comprehensive list of such words, paired with their meanings and examples, to help you distinguish between them effectively.
Commonly Confused Words
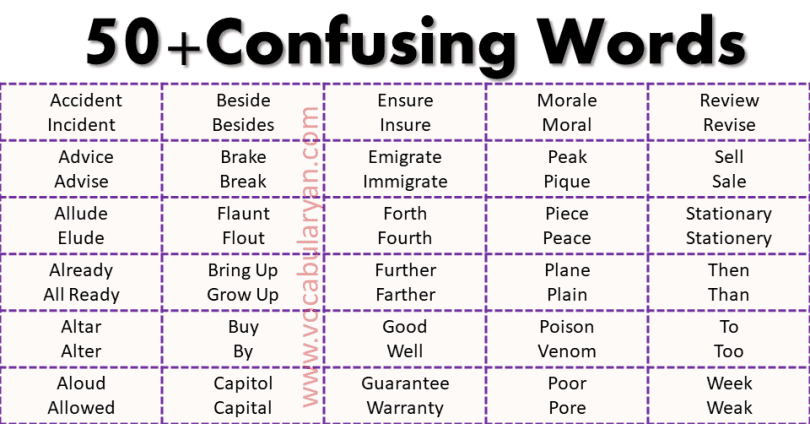
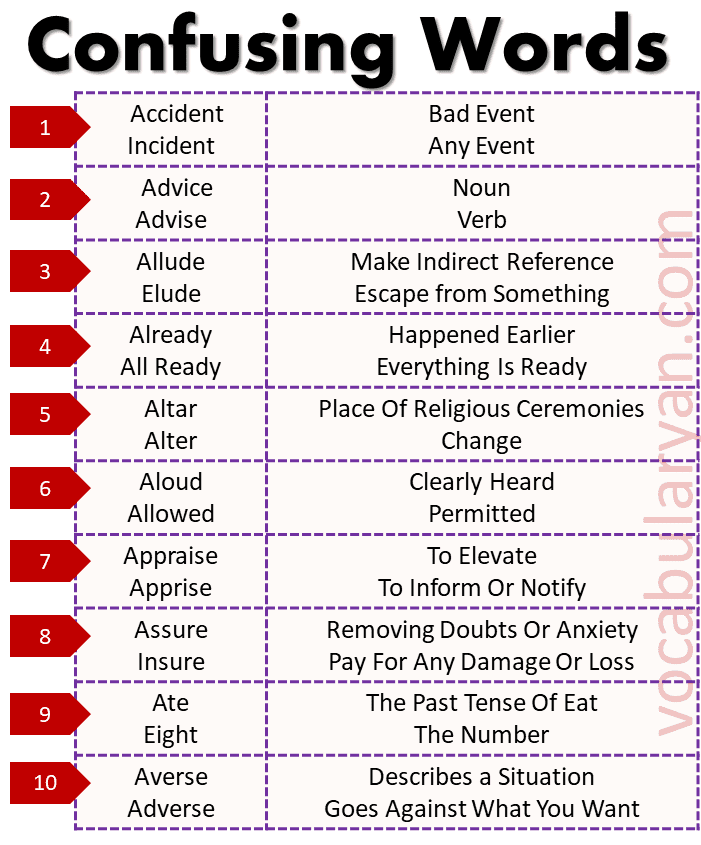
Accident vs. Incident:
- Accident: A bad or unfortunate event.
Example: The car accident caused a major traffic jam. - Incident: Any event, often without negative connotations.
Example: The incident was reported to the authorities.
Advice vs. Advise:
- Advice: A noun meaning guidance or recommendations.
Example: I need your advice on this matter. - Advise: A verb meaning to recommend or offer guidance.
Example: She advised me to take the shortcut.
Allude vs. Elude:
- Allude: To make an indirect reference.
Example: He alluded to his previous achievements. - Elude: To escape from something.
Example: The thief managed to elude the police.
Already vs. All Ready:
- Already: Happened earlier.
Example: I have already completed the project. - All Ready: Everything is prepared.
Example: We are all ready to leave.
Altar vs. Alter:
- Altar: A place for religious ceremonies.
Example: The couple exchanged vows at the altar. - Alter: To change something.
Example: Can you alter this dress to fit me?
Aloud vs. Allowed:
- Aloud: Clearly heard.
Example: She read the poem aloud to the class. - Allowed: Permitted.
Example: Smoking is not allowed in this building.
Appraise vs. Apprise:
- Appraise: To evaluate or assess.
Example: The jeweler appraised the diamond ring. - Apprise: To inform or notify.
Example: Please apprise me of any changes to the schedule.
Assure vs. Insure:
- Assure: To remove doubts or anxiety.
Example: I assure you everything will be fine. - Insure: To pay for any damage or loss.
Example: Did you insure your car?
Ate vs. Eight:
- Ate: The past tense of eat.
Example: I ate breakfast late this morning. - Eight: The number.
Example: She has eight pencils on her desk.
Averse vs. Adverse:
- Averse: Disliking or unwilling.
Example: She is averse to taking unnecessary risks. - Adverse: Harmful or unfavorable.
Example: The medication had adverse side effects.
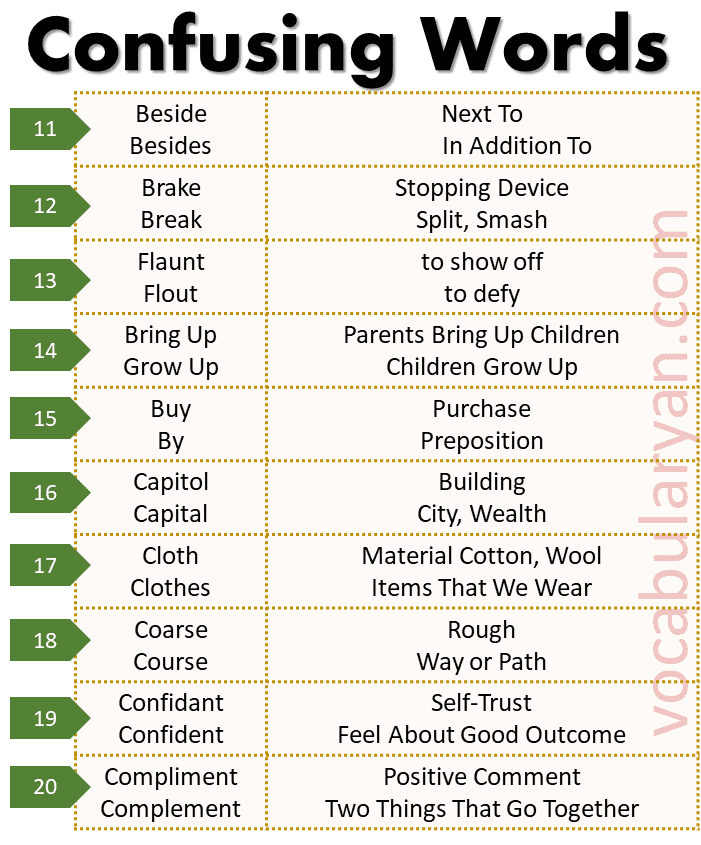
Beside vs. Besides:
- Beside: Next to.
Example: He sat beside me during the movie. - Besides: In addition to.
Example: Besides painting, she enjoys sculpting.
Been vs. Gone:
- Been: You have traveled and returned.
Example: I have been to Paris twice. - Gone: You have traveled and not yet returned.
Example: She has gone to the store.
Brake vs. Break:
- Brake: A stopping device.
Example: He pressed the brake to avoid the collision. - Break: To split or smash something.
Example: Be careful not to break the glass.
Bring Up vs. Grow Up:
- Bring Up: To raise children.
Example: Parents bring up their kids with love and care. - Grow Up: For children to mature.
Example: Kids grow up so quickly.
Buy vs. By:
- Buy: To purchase.
Example: I need to buy groceries. - By: A preposition indicating proximity or agency.
Example: This book is written by a famous author.
Capitol vs. Capital:
- Capitol: A building for legislative activities.
Example: The Capitol building is located in Washington, D.C. - Capital: A city or wealth.
Example: Paris is the capital of France.
Cloth vs. Clothes:
- Cloth: Material like cotton or wool.
Example: The tailor used a fine cloth for the suit. - Clothes: Items we wear.
Example: She bought new clothes for the event.
Coarse vs. Course:
- Coarse: Rough or unrefined.
Example: The sandpaper is coarse. - Course: A way or path.
Example: He took a different course to avoid traffic.
Confidant vs. Confident:
- Confidant: Someone you trust.
Example: She is my confidant in all matters. - Confident: Feeling assured about a good outcome.
Example: He is confident about passing the test.
Compliment vs. Complement:
- Compliment: A positive comment.
Example: She gave me a compliment on my dress. - Complement: Two things that go well together.
Example: The red wine complements the steak perfectly.
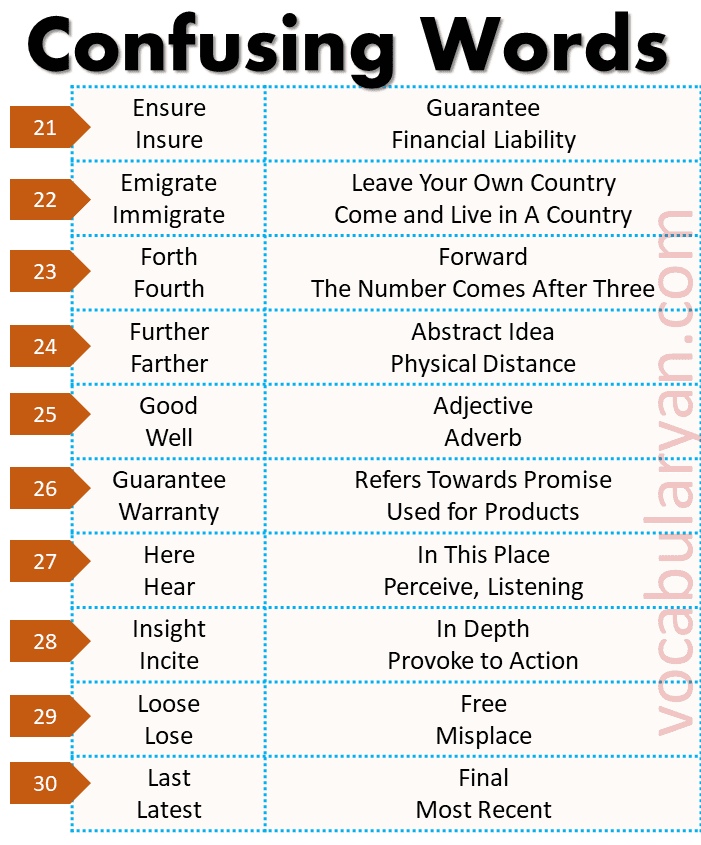
Ensure vs. Insure:
- Ensure: To guarantee.
Example: Please ensure that the door is locked. - Insure: To cover financial liability.
Example: Did you insure your house against floods?
Emigrate vs. Immigrate:
- Emigrate: To leave your country.
Example: They decided to emigrate to Canada. - Immigrate: To come to live in a country.
Example: Many people immigrate to the U.S. for better opportunities.
Forth vs. Fourth:
- Forth: Forward.
Example: He came forth to volunteer. - Fourth: The number after three.
Example: She finished in fourth place.
Further vs. Farther:
- Further: For abstract ideas.
Example: Let’s discuss this further. - Farther: For physical distance.
Example: He walked farther than anyone else.
Good vs. Well:
- Good: An adjective describing quality.
Example: She is a good artist. - Well: An adverb describing how something is done.
Example: He performs well under pressure.
Guarantee vs. Warranty:
- Guarantee: A promise.
Example: We guarantee satisfaction. - Warranty: A product’s assurance.
Example: This laptop comes with a two-year warranty.
Here vs. Hear:
- Here: In this place.
Example: Please sit here. - Hear: To perceive sound.
Example: Can you hear the music?
House vs. Home:
- House: A building.
Example: That house has been empty for years. - Home: A place where you live.
Example: This is my home.
Insight vs. Incite:
- Insight: In-depth understanding.
Example: She provided valuable insight into the problem. - Incite: To provoke action.
Example: His speech incited a lot of debates.
Last vs. Latest:
- Last: Final.
Example: This is the last chapter of the book. - Latest: Most recent.
Example: Have you seen the latest movie?
Loose vs. Lose:
- Loose: Not tight.
Example: This shirt is too loose. - Lose: To misplace or not win.
Example: Don’t lose your keys.
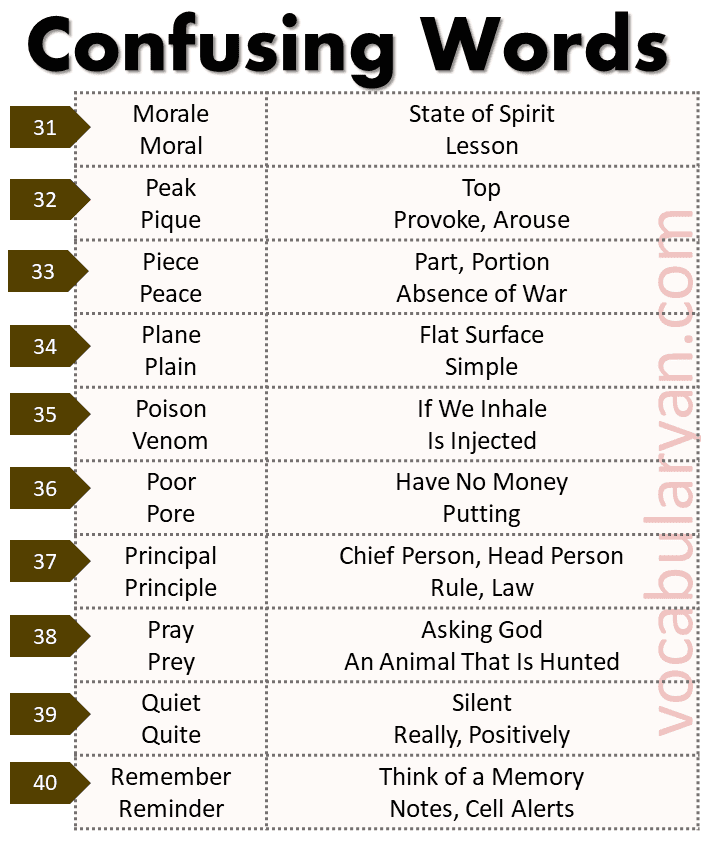
Morale vs. Moral:
- Morale: State of spirit.
Example: The team’s morale was high after the win. - Moral: A lesson.
Example: The moral of the story is to be kind.
Peak vs. Pique:
- Peak: The top.
Example: They reached the peak of the mountain. - Pique: To provoke or arouse.
Example: His curiosity was piqued by the mysterious letter.
Piece vs. Peace:
- Piece: A part or portion.
Example: Can I have a piece of cake? - Peace: Absence of war.
Example: They signed a peace treaty.
Plane vs. Plain:
- Plane: A flat surface.
Example: The carpenter smoothed the plane of the table. - Plain: Simple or unadorned.
Example: She prefers plain clothing.
Poison vs. Venom:
- Poison: A substance that is harmful when ingested or inhaled.
Example: The plant contains poison. - Venom: A substance injected by an animal.
Example: The snake’s venom is deadly.
Poor vs. Pore:
- Poor: Lacking money.
Example: They grew up in a poor family. - Pore: A small opening in the skin.
Example: Sweat comes out through pores.
Principal vs. Principle:
- Principal: The head of a school or chief person.
Example: The principal gave a speech. - Principle: A rule or law.
Example: The principle of fairness is important.
Pray vs. Prey:
- Pray: To ask God.
Example: Let’s pray for a good outcome. - Prey: An animal hunted by another.
Example: The lion caught its prey.
Quiet vs. Quite:
- Quiet: Silent.
Example: Please be quiet in the library. - Quite: Really or positively.
Example: The movie was quite interesting.
Remember vs. Reminder:
- Remember: To think of a memory.
Example: I remember our trip to the beach. - Reminder: Notes or alerts.
Example: Set a reminder for the meeting.
Review vs. Revise:
- Review: To examine.
Example: I need to review my notes before the exam. - Revise: To correct errors.
Example: Please revise this draft for accuracy.
Sell vs. Sale:
- Sell: A verb meaning to exchange for money.
Example: They sell fresh vegetables. - Sale: A noun meaning the act of selling.
Example: The store has a sale this weekend.
Stationary vs. Stationery:
- Stationary: Not moving.
Example: The car remained stationary at the traffic light. - Stationery: Writing materials.
Example: She bought new stationery for school.
Then vs. Than:
- Then: At that time.
Example: We went to dinner and then to a movie. - Than: For comparison.
Example: He is taller than his brother.
To vs. Too:
- To: In the direction of something.
Example: Let’s go to the park. - Too: Also or excessively.
Example: I want to come too.
Week vs. Weak:
- Week: Seven days.
Example: She will visit next week. - Weak: Lacking strength.
Example: He felt weak after the workout.
Whether vs. Weather:
- Whether: If or in case.
Example: I don’t know whether she will join us. - Weather: The atmosphere or climate.
Example: The weather is sunny today.
Whom vs. Who:
- Whom: Refers to the object of a sentence.
Example: Whom did you call yesterday? - Who: Refers to the subject of a sentence.
Example: Who is coming to the party?
Witch vs. Which:
- Witch: A sorceress.
Example: The witch cast a spell. - Which: Refers to a choice.
Example: Which dress do you prefer?




Leave a Comment