Talking about plants and Flowers using Their Botanical names is like using a secret code that plant scientists and enthusiasts all over the world understand. These names are important because they stay the same no matter where you are.
Imagine this! In different places, people might have different names for the same flower. This can be confusing! But with scientific names, there’s no confusion. Everyone knows exactly which flower you’re talking about.
Let’s take an example. You know the Rose, right? Well, its Botanical name is ‘Rosa’. And what about the Sunflower? Its special scientific name is ‘Helianthus annuus’. These names give us more information about the flower and where it comes from.
So, when we use Scientific Names for Flowers, we’re sure about which flower we mean. It’s an easy way to share information without getting mixed up. If you’re curious about plants, learning their scientific names is a great way to start your plant adventure!
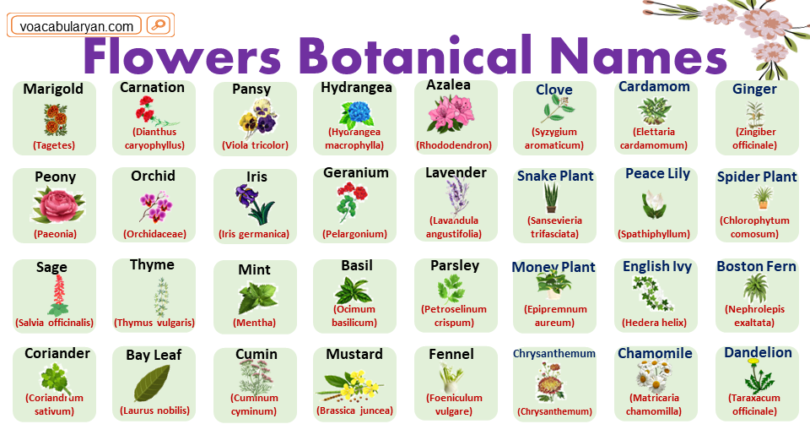
List of Botanical Flower Names
- Rose (Rosa):
- Roses belong to the genus Rosa. They are flowering plants known for their thorny stems and fragrant, colorful flowers.
- Sunflower (Helianthus annuus):
- Sunflowers, scientifically named Helianthus annuus, are annual plants with large, bright yellow flower heads. They are known for turning to face the sun.
- Tulip (Tulipa):
- Tulips belong to the genus Tulipa. These bulbous plants are recognized for their cup-shaped flowers and come in various colors.
- Daffodil (Narcissus):
- Daffodils, scientifically known as Narcissus, are bulbous plants with trumpet-shaped flowers. They are typically yellow and bloom in spring.
- Lily (Lilium):
- Lilies, belonging to the genus Lilium, are flowering plants with large, showy flowers. They come in various colors and have distinct petals.
- Marigold (Tagetes):
- Marigolds are plants in the genus Tagetes. They are characterized by their bright orange or yellow flowers and are often used for ornamental purposes.
- Carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus):
- Carnations, scientifically known as Dianthus caryophyllus, are flowering plants with fringed petals and a pleasant fragrance. They come in various colors.
- Pansy (Viola tricolor):
- Pansies, belonging to the genus Viola, are plants with distinct “faces” on their flowers. They are known for their vibrant colors.
- Hydrangea (Hydrangea macrophylla):
- Hydrangeas belong to the genus Hydrangea. They are recognized for their large, clustered flowers and can change color based on soil acidity.
- Azalea (Rhododendron):
- Azaleas are flowering shrubs in the genus Rhododendron. They have colorful and often fragrant flowers.
- Peony (Paeonia):
- Peonies belong to the genus Paeonia. They are herbaceous plants known for their large, often fragrant flowers.
- Orchid (Orchidaceae):
- Orchids belong to the family Orchidaceae. They are diverse flowering plants known for their intricate and exotic blooms.
- Iris (Iris germanica):
- Scientific Description: Irises belong to the genus Iris. They have distinctive, sword-shaped leaves and come in a variety of colors.
- Geranium (Pelargonium):
- Geraniums belong to the genus Pelargonium. They are flowering plants with clusters of colorful flowers and are commonly used as ornamentals.
- Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia):
- Lavender belongs to the genus Lavandula. It is known for its fragrant, narrow spikes of purple flowers and is often used in aromatherapy.
- Sage (Salvia officinalis):
- Sage belongs to the genus Salvia. It is a herb with gray-green leaves and spikes of blue to purple flowers, commonly used in cooking.
- Thyme (Thymus vulgaris):
- Thyme belongs to the genus Thymus. It is a low-growing herb with small leaves and is used to add flavor to various dishes.
- Mint (Mentha):
- Mint belongs to the genus Mentha. It is a fragrant herb with green leaves, commonly used in cooking and beverages.
- Basil (Ocimum basilicum):
- Basil belongs to the genus Ocimum. It is an aromatic herb with green leaves, often used in Mediterranean cuisine.
- Parsley (Petroselinum crispum):
- Parsley belongs to the genus Petroselinum. It has curly or flat leaves and is commonly used as a garnish in cooking.
- Coriander (Coriandrum sativum):
- Coriander belongs to the genus Coriandrum. It is an herb with aromatic leaves and seeds, commonly used in culinary dishes.
- Bay Leaf (Laurus nobilis):
- Bay leaves come from the Bay Laurel tree, scientifically known as Laurus nobilis. They are used to add flavor to various dishes.
- Cumin (Cuminum cyminum):
- Cumin belongs to the genus Cuminum. It is a spice with aromatic seeds, commonly used in cooking, especially in Indian and Middle Eastern cuisines.
- Mustard (Brassica juncea):
- Mustard plants belong to the genus Brassica. They produce seeds used to make the condiment mustard, and their leaves are edible.
- Fennel (Foeniculum vulgare):
- Fennel belongs to the genus Foeniculum. It is an herb with feathery leaves and a licorice-like flavor, used in cooking.
- Clove (Syzygium aromaticum):
- come from the tree Syzygium aromaticum. They are aromatic flower buds used as a spice.
- Cardamom (Elettaria cardamomum):
- Cardamom belongs to the genus Elettaria. It is a spice with a strong, sweet aroma, used in both sweet and savory dishes.
- Ginger (Zingiber officinale):
- Ginger belongs to the genus Zingiber. It is a rhizome with a spicy and aromatic flavor, commonly used in cooking and for its medicinal properties.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa):
- Turmeric belongs to the genus Curcuma. It is a bright yellow spice with a warm and slightly bitter taste, commonly used in curry dishes.
- Aloe Vera (Aloe barbadensis):
- Aloe vera belongs to the species Aloe barbadensis. It is a succulent plant known for its gel-filled leaves, often used for skin-related benefits.
- Snake Plant (Sansevieria trifasciata):
- Snake plants belong to the species Sansevieria trifasciata. They have long, upright leaves and are easy to care for, making them popular indoor plants.
- Peace Lily (Spathiphyllum):
- Peace lilies belong to the genus Spathiphyllum. They have elegant, white flowers and are known for their air-purifying qualities, making them popular indoor plants.
- Spider Plant (Chlorophytum comosum):
- Spider plants belong to the species Chlorophytum comosum. They have arching leaves and produce baby plantlets, making them easy to grow indoors.
- Rubber Plant (Ficus elastica):
- Rubber plants belong to the species Ficus elastica. They have large, glossy leaves and are popular as indoor trees, known for their easy care.
- Pothos (Epipremnum aureum):
- Pothos belong to the species Epipremnum aureum. Also known as Devil’s Ivy, they are trailing plants with heart-shaped leaves and are easy to grow indoors.
- Money Plant (Epipremnum aureum):
- Money plants, also known as Golden Pothos, belong to the species Epipremnum aureum. They have heart-shaped leaves and are believed to bring good luck, making them popular indoor plants.
- English Ivy (Hedera helix):
- English Ivy, scientifically known as Hedera helix, is a climbing vine with distinctive lobed leaves. It is often used for ground cover or as an ornamental plant.
- Boston Fern (Nephrolepis exaltata):
- Boston Ferns belong to the species Nephrolepis exaltata. They are feathery-leafed ferns commonly used as ornamental houseplants.
- Philodendron (Philodendron hederaceum):
- Philodendrons belong to the species Philodendron hederaceum. They are popular indoor plants with heart-shaped leaves and are easy to care for.
- African Violet (Saintpaulia):
- African Violets belong to the genus Saintpaulia. They are small, flowering plants with fuzzy leaves and colorful flowers, commonly kept as houseplants.
- Chrysanthemum (Chrysanthemum):
- Chrysanthemums belong to the genus Chrysanthemum. They are flowering plants with a variety of shapes and colors, often used for decorative purposes.
- Dandelion (Taraxacum officinale):
- Dandelions, scientifically known as Taraxacum officinale, are flowering plants with distinctive yellow flowers and seed heads. They are both considered weeds and have medicinal uses.
- Chamomile (Matricaria chamomilla):
- Chamomile is an herb with small, daisy-like flowers. It is often used to make a calming tea.
- Echinacea (Echinacea purpurea):
- Echinacea, or coneflower, has pink-purple petals and is known for its immune-boosting properties.
- Black Cohosh (Actaea racemosa):
- Black cohosh is a plant with tall spikes of white flowers. It is used in traditional medicine for various purposes.
- Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba):
- Ginkgo is a unique tree with fan-shaped leaves. Its extracts are used in traditional medicine and supplements.
- Ginseng (Panax ginseng):
- Scientific Description: Ginseng is a root known for its adaptogenic properties. It is often used in traditional medicine for various health benefits.
- Milk Thistle (Silybum marianum):
- : Milk thistle is a plant with prickly leaves and purple flowers. It is believed to have liver-protective properties.
- John’s Wort (Hypericum perforatum):
- John’s Wort is a flowering plant used in herbal medicine for its potential antidepressant properties.
Types of Flowers
Flowers are the parts of plants that help them make new plants. Most plants on Earth are called angiosperms, and they have flowers. These flowers are super important for the plants to have babies.
Now, let’s talk about different kinds of flowers. Imagine flowers like a big family with many members, and they each have their own unique features.
- Complete Flowers:
- Explanation: These flowers have all the parts they need — the outer leaves, inner leaves, pollen-makers, and seed-makers.
- Example: Roses and lilies.
- Incomplete Flowers:
- Explanation: Some flowers are missing a part or two — they might not have outer leaves, inner leaves, pollen-makers, or seed-makers.
- Example: Grass flowers.
- Perfect Flowers:
- Explanation: Perfect flowers have both pollen-makers and seed-makers in one flower.
- Example: Sunflowers and roses.
- Imperfect Flowers:
- Explanation: Imperfect flowers are missing either the pollen-makers or the seed-makers.
- Example: Squash and holly flowers.
- Monoecious Plants:
- Explanation: Some plants have both boy and girl flowers on the same plant.
- Example: Corn and zucchini plants.
- Dioecious Plants:
- Explanation: Other plants have boy and girl flowers on different plants.
- Example: Kiwi and holly plants.
- Inflorescence:
- Explanation: Inflorescence means many flowers grouped together on one stem.
- Example: Sunflower and daisy clusters.
- Ray Flowers and Disk Flowers:
- Explanation: In some flowers, there are petals around the edge (ray flowers) and others in the middle (disk flowers).
- Example: Sunflowers have both ray and disk flowers.
- Actinomorphic Flowers:
- Explanation: These flowers have parts that are the same all around, like a circle.
- Example: Lilies and roses.
- Zygomorphic Flowers:
- Explanation: These flowers have parts that are different on each side.
- Example: Orchids and snapdragons.
- Petaloid Monocots:
- Explanation: Some flowers that are usually simple have petal-like parts.
- Example: Tulips and lilies.





Leave a Comment