Learning the types of adverbs is important for understanding how to describe actions clearly in English. Adverbs tell us how, when, where, how often, and to what extent something happens. Common types include adverbs of manner (e.g., quickly, slowly), adverbs of time (e.g., now, yesterday), adverbs of place (e.g., here, everywhere), adverbs of frequency (e.g., always, often), and adverbs of degree (e.g., very, almost). Knowing these adverb types helps improve grammar, sentence structure, and overall communication skills.
What Are Adverbs?
An adverb is a part of speech that functions to modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs by providing information about the manner, degree, time, place, or frequency of an action or state. Adverbs contribute to the precision and clarity of communication, enhancing the overall meaning and tone of a sentence.
Types of Adverb
Adverbs are words that describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. The main types include adverbs of time (when), place (where), manner (how), degree (how much), and frequency (how often). Each type gives more detail to actions or descriptions in a sentence.
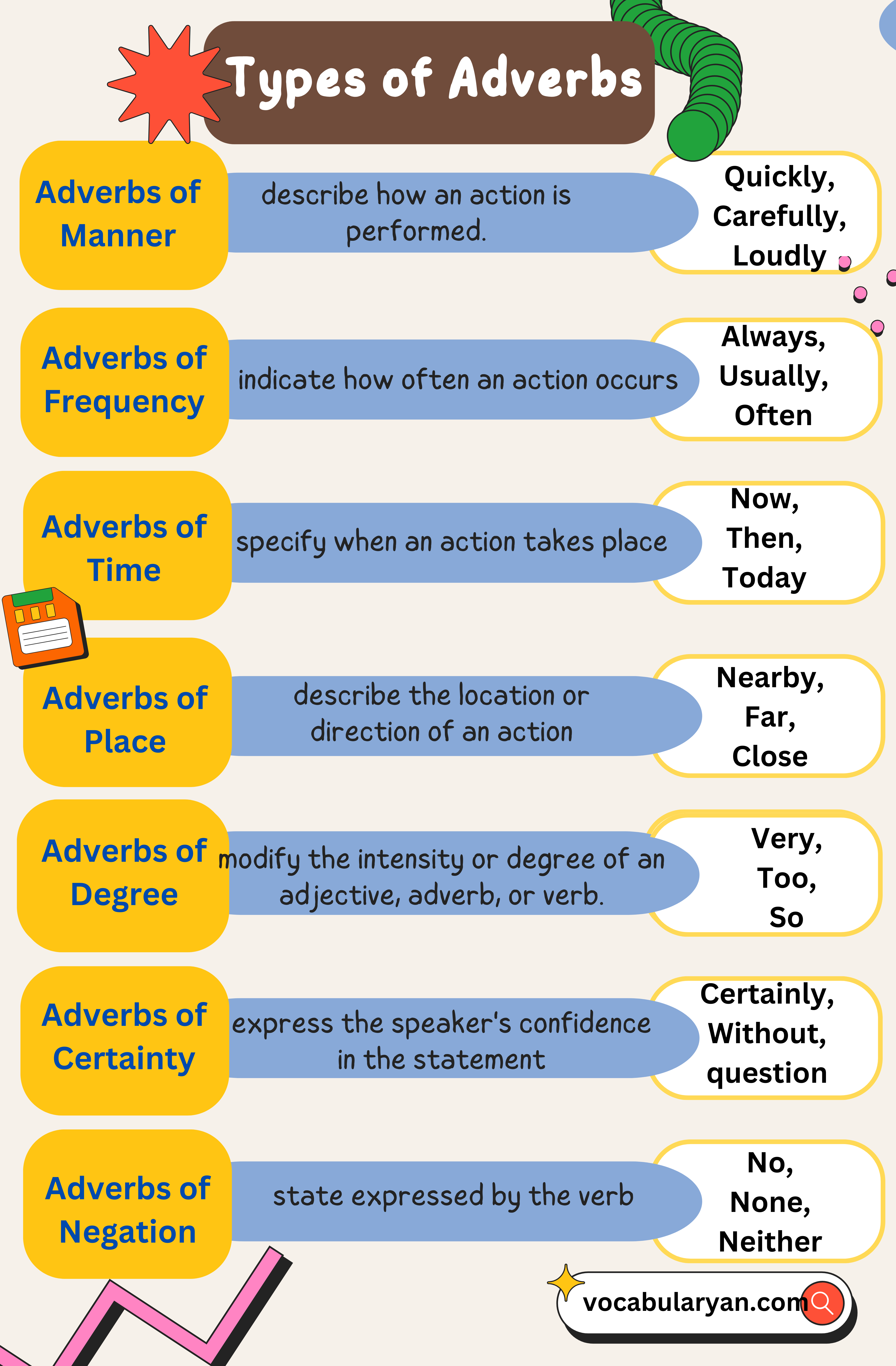
1. Adverbs of Manner
Explanation: These adverbs describe how an action is performed. They often answer the question “how.”
Example: She sang beautifully. (How did she sing? Beautifully.)
2. Adverbs of Frequency
Explanation: These adverbs indicate how often an action occurs. They answer the question “how often.”
Example: He always arrives on time. (How often does he arrive on time? Always.)
3. Adverbs of Time
Explanation: These adverbs specify when an action takes place. They answer the question “when.”
Example: We will meet tomorrow. (When will we meet? Tomorrow.)
4. Adverbs of Place
Explanation: These adverbs describe the location or direction of an action. They answer the question “where.”
Example: The cat is sitting upstairs. (Where is the cat sitting? Upstairs.)
5. Adverbs of Degree
Explanation: These adverbs modify the intensity or degree of an adjective, adverb, or verb. They answer the question “to what extent.”
Example: It’s too hot today. (To what extent is it hot? Too hot.)
6. Adverbs of Certainty
Explanation: These adverbs express the speaker’s confidence or certainty in the statement.
Example: Certainly, he will be here soon.
7. Adverbs of Negation
Explanation: These adverbs deny the action or state expressed by the verb.
Example: She does not speak loudly.
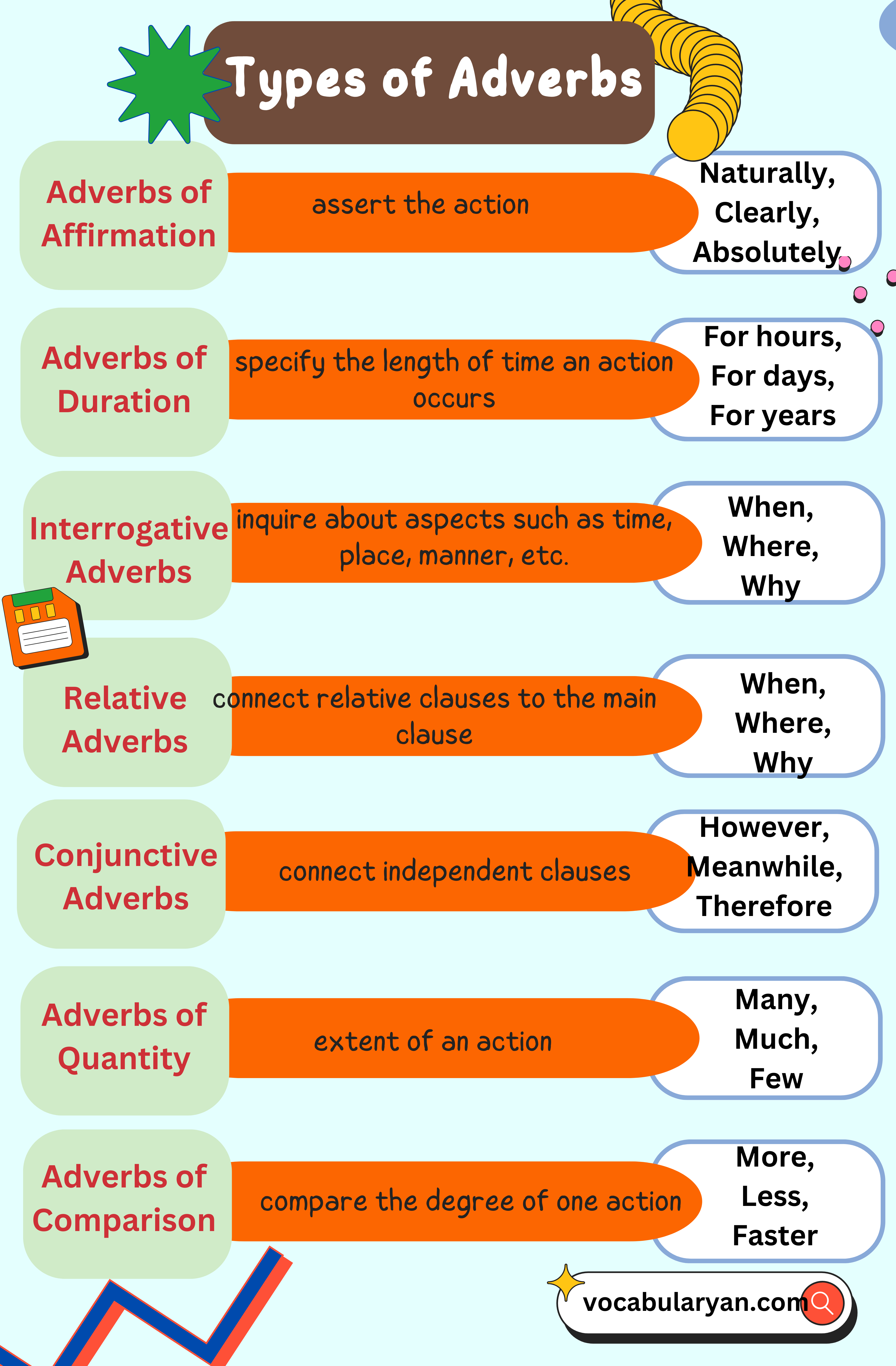
8. Adverbs of Affirmation
Explanation: These adverbs confirm or assert the action or state expressed by the verb.
Example: He knows the answer.
9. Adverbs of Duration
Explanation: These adverbs specify the length of time an action occurs. They answer the question “how long.”
Example: They worked hard throughout the night. (How long did they work? Throughout the night.)
10. Interrogative Adverbs
Explanation: These adverbs introduce questions and inquire about aspects such as time, place, manner, etc.
Example: When will they arrive?
11. Relative Adverbs
Explanation: These adverbs connect relative clauses to the main clause and indicate time, place, or reason.
Example: This is the place where it happened.
12. Conjunctive Adverbs
Explanation: These adverbs connect independent clauses and show relationships like contrast, cause and effect, etc.
Example: However, I disagree with your opinion.
13. Adverbs of Quantity
Explanation: These adverbs specify the amount or extent of an action.
Example: She has too many books.
14. Adverbs of Comparison
Explanation: These adverbs compare the degree of one action or quality to another.
Example: He runs faster than his brother.
List of Different Types of Adverbs
in this paragraph, we are providing a huge number of lists of adverbs for more understanding of adverbs of types.
| Manner | Frequency | Time | Place | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quickly | Always | Now | Here | Very |
| Slowly | Usually | Then | There | Too |
| Gracefully | Often | Today | Everywhere | So |
| Carefully | Sometimes | Tomorrow | Nowhere | Quite |
| Loudly | Occasionally | Yesterday | Somewhere | Extremely |
| Softly | Rarely | Soon | Anywhere | Absolutely |
| Patiently | Seldom | Later | Nearby | Rather |
| Briskly | Hardly ever | Early | Far | Fairly |
| Efficiently | Never | Late | Close | Almost |
| Awkwardly | Constantly | Tonight | Farther | Completely |
| Politely | Regularly | Morning | Farthest | Partially |
| Roughly | Frequently | Afternoon | Away | Nearly |
| Gently | Intermittently | Evening | Above | Barely |
| Hastily | Periodically | Afterward(s) | Below | Entirely |
| Casually | Daily | Before | Within | Utterly |
| Elegantly | Weekly | After | Outside | Well |
| Confidently | Monthly | Recently | Inside | Enough |
| Cheerfully | Yearly | Presently | Upstairs | Exceedingly |
| Quietly | Biweekly | Currently | Downstairs | Certainly |
You May Also Like
