Nouns are like naming words. They’re often the first things you learn about in English class. They’re important because they give names to everything we can sense with our five senses: touch, see, smell, taste, hear, or hold. So, if you can point to it, describe it, or experience it, chances are it’s a noun!
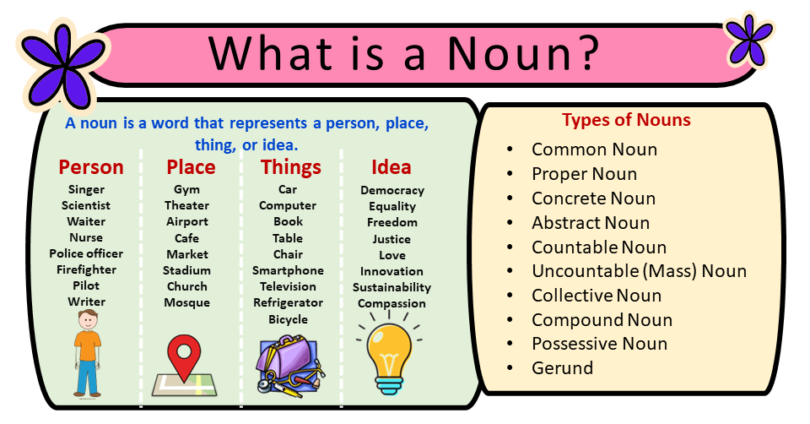
What is a Noun?
A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. It could be anything you can see, touch, hear, taste, or smell. For example, “dog,” “house,” “love,” and “friend” are all nouns. Nouns are like labels that we use to talk about our world’s people, objects, or concepts.
Types of Nouns:
Nouns can be classified into several types based on their roles and characteristics. Here are some common types of nouns:
1:Common Nouns
These are general names for people, places, things, or ideas.
Examples: “dog,” “city,” “book,” and “happiness.”
2:Proper Nouns:
These are specific names for individual people, places, or things and are typically capitalized.
Examples: “John,” “Paris,” “The Great Gatsby,” and “Coca-Cola.”
3:Concrete Nouns:
These are nouns that refer to things that can be perceived through the senses (sight, hearing, touch, taste, or smell).
Examples: “table,” “music,” “tree,” and “chocolate.”
4:Abstract Nouns:
These are nouns that refer to ideas, concepts, feelings, or qualities that cannot be perceived through the senses.
Examples: “love,” “happiness,” “freedom,” and “justice.”
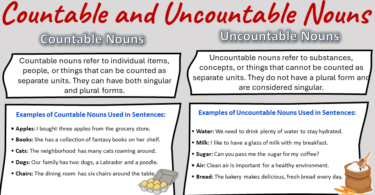
5:Countable Nouns:
These nouns can be counted and have both singular and plural forms.
Examples: “car” (singular) and “cars” (plural), “apple” (singular) and “apples” (plural).
6: Uncountable (Mass) Nouns:
These are nouns that cannot be counted individually and do not have a plural form.
Examples: “water,” “rice,” “knowledge,” and “money.”
7: Collective Nouns:
These are nouns that refer to groups of people or things as a single unit.
Examples: “team,” “herd,” “family,” and “flock.”
8: Compound Nouns:
These are nouns formed by combining two or more words.
Examples: “toothpaste,” “bluebird,” “firefighter,” and “mother-in-law.”
Example of Noun Sentences
- The dog barked loudly.
- We picnicked in the garden.
- The car zoomed by.
- My phone buzzed often.
- The teacher taught well.
- We hiked the forest.
- The coffee was good.
- My shoes were worn.
- The sun set beautifully.
- The computer showed data.
- A kite flew high.
- The movie was crowded.
- The artifact amazed him.
- The restaurant served diverse dishes.
- The music played loud.
- The river flowed gently.
- She studied constellations.
- The bicycle raced downhill.
- The painter worked diligently.
- The airplane flew swiftly.
Nouns Used as Different Components of a Sentence
These are some common ways in which nouns are used as different components of a sentence, helping to convey meaning and structure.
1: Subject: The subject of a sentence is the noun or noun phrase that performs the action of the verb or is described by the verb.
Example:
- “The cat” chased the mouse.
- “My friend” likes to play basketball.
2: Direct Object: The direct object receives the action of the verb. It answers the question “What?” or “Whom?” after the action verb.
Example:
- I bought “a book.”
- She painted “the wall.”
3: Indirect Object: The indirect object is the recipient of the direct object. It answers the question “To whom?” or “For whom?” or “To what?” or “For what?” after the action verb. Example:
- He gave “me” “a gift.”
- She made “us” and “some cookies.”
4: Object of a Preposition: A noun can also be the object of a preposition, which is a word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and another word in the sentence.
Example:
- The book is “on” “the table.”
- She walked “to” “the park.”
5: Predicate Nominative (Subject Complement): A predicate nominative follows a linking verb and renames or identifies the subject of a sentence.
Example:
- She is “a doctor.”
- The winner of the contest was “Jane.”
6: Appositive: An appositive is a noun or noun phrase that renames or further identifies another noun right beside it.
Example:
- My friend, “Tom,” is coming over.
- My favorite fruit, “apples,” is nutritious.
You May Also Like to Read





Leave a Comment