Learning Conjunctive Adverbs is important for connecting ideas and improving sentence flow in English. These adverbs link independent clauses and show relationships like contrast, cause, time, or addition. Common examples include however, therefore, moreover, consequently, and meanwhile. For instance: “She was tired; however, she finished her work.” Conjunctive adverbs are often followed by a comma and help make writing more formal and logical. Whether you’re writing essays, reports, or speaking clearly, using conjunctive adverbs enhances coherence and clarity in communication.
Definition of Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs are words that connect two independent clauses and show relationships like contrast, cause, effect, or sequence. Examples include however, therefore, moreover, meanwhile, and consequently. They help sentences flow smoothly and add clarity between ideas.
Usage of Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive Adverbs usage helps to convey relationships such as contrast, cause and effect, addition, comparison, time sequence, and more. Here are some common ways in which conjunctive adverbs are used:
1. Contrast:
Examples: However, nevertheless, nonetheless, on the other hand.
- Usage: To introduce a contrasting idea or to acknowledge a counterpoint.
- Example: The weather was cold; however, they decided to go for a swim.
2. Cause and Effect:
Examples: Therefore, thus, hence, consequently.
- Usage: To indicate a cause-and-effect relationship between two clauses.
- Example: She missed the train; consequently, she arrived late to the meeting.
3. Addition:
Examples: Moreover, furthermore, additionally, in addition.
- Usage: To add information, emphasize a point, or introduce an additional idea.
- Example: The presentation was well-organized; moreover, the visuals were compelling.
4. Comparison:
Examples: Similarly, likewise.
- Usage: To show a similarity or comparison between two ideas.
- Example: The two theories are based on similar principles; likewise, they share common limitations.
5. Time Sequence:
Examples: Meanwhile, afterward, subsequently, then.
- Usage: To indicate the order of events or actions.
- Example: She submitted the proposal; meanwhile, the team started working on the project.
6. Clarification:
Examples: Indeed, certainly.
- Usage: To provide additional information or emphasize the truth of a statement.
- Example: The experiment was successful; in fact, it exceeded our expectations.
7. Summarizing:
Examples: In conclusion, overall, to sum up.
- Usage: To signal a summary or a final point.
- Example: The report covered various aspects of the project; in conclusion, it highlighted the key achievements.
8. Transition:
Examples: Next, meanwhile, on the contrary.
- Usage: To guide the reader from one idea or point to the next.
- Example: The first chapter discussed the background; next, we will explore the methodology.
9. Emphasis:
Examples: Indeed, certainly.
- Usage: To add emphasis or strengthen a statement.
- Example: The results were surprising; indeed, they challenged the existing theories.
10. Sequence and Order:
Examples: First, secondly, finally, last.
- Usage: To organize ideas in a sequential or ordered manner.
- Example: Firstly, we need to gather the data; secondly, we will analyze it; finally, we will conclude.
List of Conjunctive Adverbs With Examples
Some common conjunctive adverbs along with their typical usage:
- However:
- Usage: Indicates a contrast or unexpected result.
- Example: She worked hard; however, she didn’t achieve the desired outcome.
- Therefore:
- Usage: Shows a cause-and-effect relationship.
- Example: The experiment was successful; therefore, the hypothesis was supported.
- Meanwhile:
- Usage: Indicates a simultaneous occurrence of events.
- Example: She was studying; meanwhile, her friends were playing outside.
- Moreover:
- Usage: Adds information or emphasizes a point.
- Example: The report was comprehensive; moreover, the visuals enhanced its overall impact.
- Nevertheless:
- Usage: Acknowledges a contrast but emphasizes the continuation of the main idea.
- Example: The task was challenging; nevertheless, he persevered and completed it.
- Furthermore:
- Usage: Adds more information or extends a point.
- Example: The company achieved its sales target; furthermore, it expanded its market presence.
- Consequently:
- Usage: Indicates a logical result or conclusion.
- Example: They missed the train; consequently, they had to find an alternative mode of transportation.
- On the other hand:
- Usage: Introduces an opposing or contrasting point.
- Example: The budget is tight; on the other hand, we cannot compromise on quality.
- In addition:
- Usage: Introduces extra information or another point.
- Example: She has excellent communication skills. In addition, she is proficient in multiple languages.
- Nonetheless:
- Usage: Similar to “nevertheless,” acknowledges a contrast.
- Example: The movie was lengthy; nonetheless, it captivated the audience until the end.
- Similarly:
- Usage: Shows a similarity or comparison.
- Example: The two projects followed a similar approach. Similarly, they encountered comparable challenges.
- Hence:
- Usage: Indicates a consequence or inference.
- Example: The data supports our hypothesis; hence, we can confidently draw our conclusions.
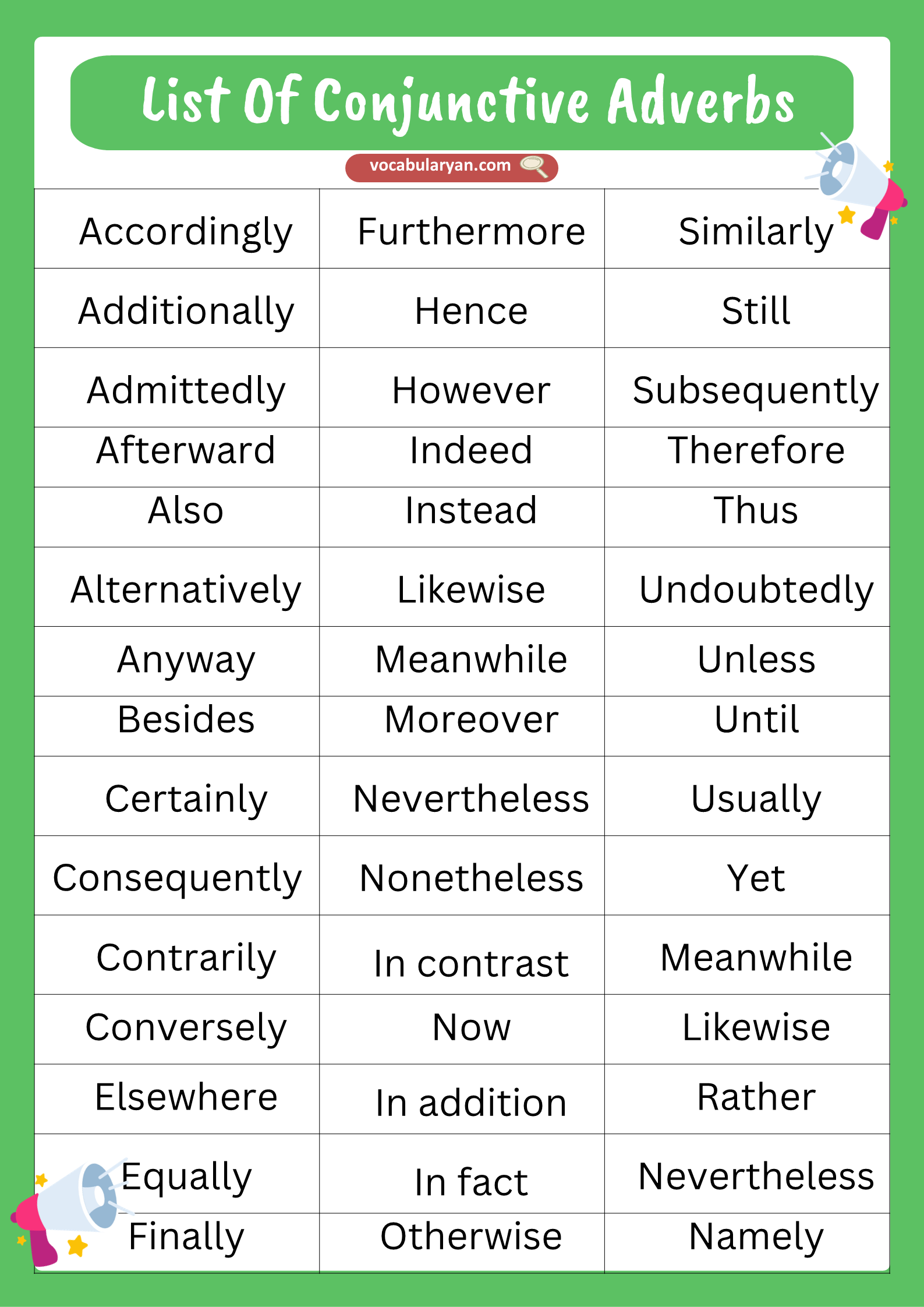
List Of Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs help link ideas and show relationships such as cause, contrast, time, or addition. Common examples include however, therefore, moreover, nevertheless, meanwhile, consequently, furthermore, otherwise, instead, and likewise. These words often come at the beginning of a sentence and are followed by a comma.
- Accordingly
- Additionally
- Admittedly
- Afterward
- Also
- Alternatively
- Anyway
- Besides
- Certainly
- Consequently
- Contrarily
- Conversely
- Elsewhere
- Equally
- Finally
- Furthermore
- Hence
- However
- Indeed
- Instead
- Likewise
- Meanwhile
- Moreover
- Nevertheless
- Nonetheless
- Notwithstanding
- Now
- On the contrary
- On the other hand
- Otherwise
- Similarly
- Still
- Subsequently
- Therefore
- Thus
- Undoubtedly
- Unless
- Until
- Usually
- Yet
- Meanwhile
- Likewise
- Rather
- Nevertheless
- Namely
- Consequently
- Ultimately
- In contrast
- In addition
- In fact
Sentences using Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs are used to connect two complete ideas and show relationships like cause, contrast, time, or addition. For example: “She was tired; however, she kept working.” or “He didn’t study; therefore, he failed the test.” These adverbs help make writing clear, smooth, and more organized by linking thoughts in a meaningful way.
- She worked hard; however, she didn’t achieve the desired result.
- We planned to go hiking; nevertheless, the rain forced us to stay indoors.
- He wanted to go to the party; therefore, he finished his work early.
- The movie was long; nonetheless, it kept the audience engaged.
- She practiced the piano for hours; furthermore, she excelled in her recital.
- The traffic was heavy; however, we managed to reach the airport on time.
- They enjoyed the concert; similarly, they loved the after-show party.
- The presentation was informative; moreover, the visuals were captivating.
- I studied for the exam; nevertheless, I felt nervous on the day.
- He forgot his lunch; consequently, he had to buy something from the cafeteria.
- She wanted to sleep in; meanwhile, her roommate was already up and about.
- She worked hard; however, she didn’t achieve the desired result.
- We planned to go hiking; nevertheless, the rain forced us to stay indoors.
- He wanted to go to the party; therefore, he finished his work early.
- The movie was long; nonetheless, it kept the audience engaged.
- She practiced the piano for hours; furthermore, she excelled in her recital.
- The traffic was heavy; however, we managed to reach the airport on time.
- They enjoyed the concert; similarly, they loved the after-show party.
- The presentation was informative; moreover, the visuals were captivating.
- I studied for the exam; nevertheless, I felt nervous on the day.
- He forgot his lunch; consequently, he had to buy something from the cafeteria.
- She wanted to sleep in; meanwhile, her roommate was already up and about.
- The instructions were clear; furthermore, the illustrations helped me understand them better.
- He missed the train; nonetheless, he arrived at the meeting just in time.
- The weather was hot; on the other hand, the pool was refreshing.
- She finished her chores; hence, she had some free time to relax.

You May Also Like
