Learning the Past Continuous tense is important for describing actions that were ongoing at a specific time in the past. It is formed using was/were + verb + -ing, such as “She was reading a book” or “They were playing soccer.” This tense helps explain background activities or events happening simultaneously in the past. Mastering the Past Continuous tense improves your ability to tell stories clearly and provide detailed descriptions of past situations in both speaking and writing.
Structures of the Tense
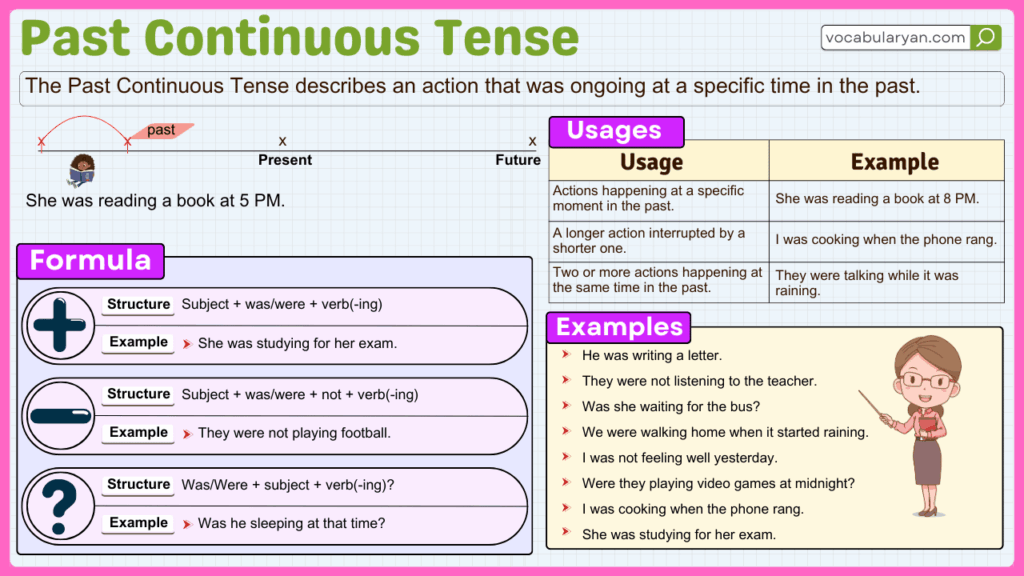
The Past Continuous Tense is formed using the helping verb “was/were” and the present participle (verb + -ing). Here’s how it works in different sentence structures:
1. Affirmative (Positive) Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + present participle (V1 + -ing)
- She was reading a book at 8 PM.
- They were playing football in the park.
- She was reading a book when I arrived.
2. Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + was/were + not + present participle (V1 + -ing)
- He wasn’t watching TV when I called.
- We weren’t studying during the break.
- They were not playing outside when it started to rain.
3. Interrogative (Question) Sentences
Structure: Was/Were + subject + present participle (V1 + -ing)?
- Was she cooking dinner at 7 PM?
- Were they talking about the project?
- Was he watching TV when you called?
4. Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Question word + was/were + subject + present participle (V1 + -ing)?
- What were you doing at 9 PM last night?
- Why was he running in the rain?
- What was she doing and why was she crying?
Subject-Verb Agreement
In the Past Continuous Tense, the helping verb “was/were” changes depending on the subject. Here’s a table to show this:
| Subject | Helping Verb |
|---|---|
| I | was |
| You | were |
| He/She/It | was |
| We | were |
| They | were |
| The dog | was |
| The dogs | were |
| My father | was |
| Sarah and John | were |
Time Expressions of Past Continuous Tense
Time expressions are essential for using the Past Continuous Tense correctly. They help clarify when the action was happening. Here are some common ones:
- While:
- She was cooking while he was watching TV.
- When:
- I was sleeping when the phone rang.
- As:
- As they were walking, it started to rain.
- At that moment:
- At that moment, he was talking to his boss.
- All day:
- She was studying all day for the exam.
- The whole time:
- They were laughing the whole time.
- From…to…:
- He was working from morning to evening.
- By that time:
- By that time, she was already waiting for us.
- Just then:
- Just then, the lights went out while we were watching a movie.
- Throughout:
- It was snowing throughout the night.
Adverb Placement
Adverbs like always, constantly, and continuously are often used with the Past Continuous Tense to emphasize ongoing actions. They usually come between “was/were” and the present participle:
Before the main verb (for adverbs of frequency)
- She was always talking during class.
- They were constantly arguing about small things.
Between “was/were” and the verb (for shorter adverbs)
- He was just leaving when I arrived.
- She was still working when I called.
At the end of the sentence (for adverbs of manner, place, or time)
- I was studying quietly in my room.
- They were playing outside all evening.
At the beginning of the sentence (for emphasis)
- Suddenly, they were running towards the exit.
- Usually, she was sleeping by this time.
Before “was/were” for emphasis
- She always was complaining about her work.
- They never were paying attention in class.
After the object or complement
- He was speaking to her politely.
- They were watching TV together.
Uses of the Past Continuous Tense
The Past Continuous Tense is such these cases:
Ongoing action in the past :
Describes an action that was happening at a particular time in the past. It emphasizes that the action was in progress during that moment.
- She was reading a book when I called.
Two simultaneous past actions :
Indicates that two actions were happening at the same time in the past, often linked by “while” or “as.”
- I was cooking while he was watching TV.
Interrupted action :
Shows that one action was already happening when another action suddenly occurred. The past continuous describes the ongoing action, and the simple past describes the interruption.
- They were playing when it started to rain.
Setting the scene in a story :
Used to describe background details in narratives, creating a vivid picture of what was happening at a certain moment.
- The wind was blowing, and the birds were singing.
Polite or indirect statements :
Makes requests, inquiries, or statements sound more polite and less direct. It is often used in conversations.
- I was wondering if you could help me.
Repeated past actions (with annoyance) :
Expresses irritation or frustration about something that happened frequently in the past, often using adverbs like “always” or “constantly.”
- He was always talking during meetings.
Future in the past :
Refers to an action that was planned or expected to happen after a certain time in the past but may or may not have happened.
- She was leaving for London the next day.
Unfinished actions in the past :
Describes something that started but was not necessarily completed. It focuses on the progress rather than the result.
- I was writing a book, but I never completed it.
Short Answers of Past Continuous Tense
Short answers are used to respond briefly to questions in the Past Continuous Tense. Here’s how they work:
| Question | Short Answer |
|---|---|
| Were you studying at 8 PM? | Yes, I was. / No, I wasn’t. |
| Was she cooking dinner? | Yes, she was. / No, she wasn’t. |
| Were they playing football? | Yes, they were. / No, they weren’t. |
| Was the dog barking? | Yes, it was. / No, it wasn’t. |
Question Tags
Question tags are short questions added to the end of statements to confirm or seek agreement. In the Past Continuous Tense, they follow the structure:
Statement + wasn’t/weren’t + subject?
- She was reading, wasn’t she?
- They weren’t playing, were they?
Examples of the Past Continuous Tense
Here are examples of the Past Continuous Tense in different forms:
- She was writing an email at 9 AM.
- They were discussing the plan during the meeting.
- He was jogging in the park when it started raining.
- She wasn’t listening to music at that time.
- They weren’t working on the project yesterday.
- He wasn’t sleeping when I called.
- Were you studying at 10 PM?
- Was she cooking dinner when you arrived?
- Were they playing football in the evening?
Common Mistakes in Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is often misused due to errors in verb forms, auxiliary verbs, and stative verbs. Many also confuse it with the simple present for routine actions.
Wrong Verb Form
- She is read a book right now. ❌
- She is reading a book right now. ✅
Forgetting the Auxiliary Verb
- They playing football in the park. ❌
- They are playing football in the park. ✅
Incorrect Negative Form
- He not listening to music at the moment. ❌
- He is not listening to music at the moment. ✅
Misusing “Being” with Action Verbs
- She is being work hard on her project. ❌
- She is working hard on her project. ✅
Using Stative Verbs Incorrectly
- I am knowing the answer to this question. ❌
- I know the answer to this question. ✅
Wrong Word Order in Questions
- Is playing she the piano at the concert? ❌
- Is she playing the piano at the concert? ✅
Using Present Continuous for Routine Actions
- He is going to school every day at 8 AM. ❌
- He goes to school every day at 8 AM. ✅
FAQs on Past Continuous Tense
1. What is the Past Continuous Tense used for?
It describes actions that were in progress at a specific time in the past or when another action interrupted them.
2. Can I use the Past Continuous Tense for completed actions?
No, it’s only for actions that were ongoing in the past. For completed actions, use the Past Simple Tense.
3. What are common time expressions used with this tense?
Now
At the moment
Right now
Currently
Nowadays
This week/month/year
At present4. When do we use the present continuous tense?
It is used for actions happening now, at the moment of speaking, or for temporary situations
5. How is the present continuous different from the simple present?
The present continuous is for actions happening now or temporary situations, while the simple present is for habits and general facts.
You May Also Like
