Present Perfect Tense! It’s a cool way to talk about past actions and when they happened. It makes your speech clear.
The Present Perfect is for things before now. We use it in English to link actions and time. Easy rules and examples are here to help you get it. You can practice more with worksheets to improve.”
What Is the Present Perfect Tense?
The present perfect tense is a verb tense used to express actions that were completed at some indefinite point in the past but have relevance to the present. It is formed by using the present tense of the auxiliary verb “have” (have/has) along with the past participle of the main verb.
Structure and Formula of the Present Perfect Tense
The basic structure of the present perfect tense is as follows:
| Subject + have/has + past participle + the rest of the sentence |
Let’s break down the structure of the present perfect tense by looking at positive, negative, interrogative, and negative interrogative sentences in a simpler way.
| Positive | Negative | Interrogative | Negative Interrogative |
| Subject + have/has + past participle + the rest of the sentence I have visited Paris.
Examples:
|
Subject + have/has + not + past participle + the rest of the sentence
Examples:
|
Have/has + subject + past participle + the rest of the sentence
Examples:
|
Have/has + subject + not + past participle + the rest of the sentence
(or) Haven’t / hasn’t + subject + past participle + the rest of the sentence Examples:
|
Time Expressions:
The present perfect tense often uses time expressions that indicate an unspecified time between the past and the present: Here are some common time expressions that are often used with the present perfect tense:
- Just: I have just finished my work. (recently)
- Already: She has already eaten lunch. (before now)
- Ever: Have you ever traveled to Europe? (at any time in your life)
- Never: They have never attended a concert. (not at any time)
- Since: I have lived here since 2010. (from a specific point in the past until now)
- For: We have known each other for ten years. (a specific duration of time)
- Recently: He has recently graduated. (in the recent past)
- In the past few days/weeks: They have accomplished a lot in the past few weeks. (recently)
- So far: We have visited three countries so far. (up to this point in time)
- This week/month/year: I have read three books this month. (in the time period specified)
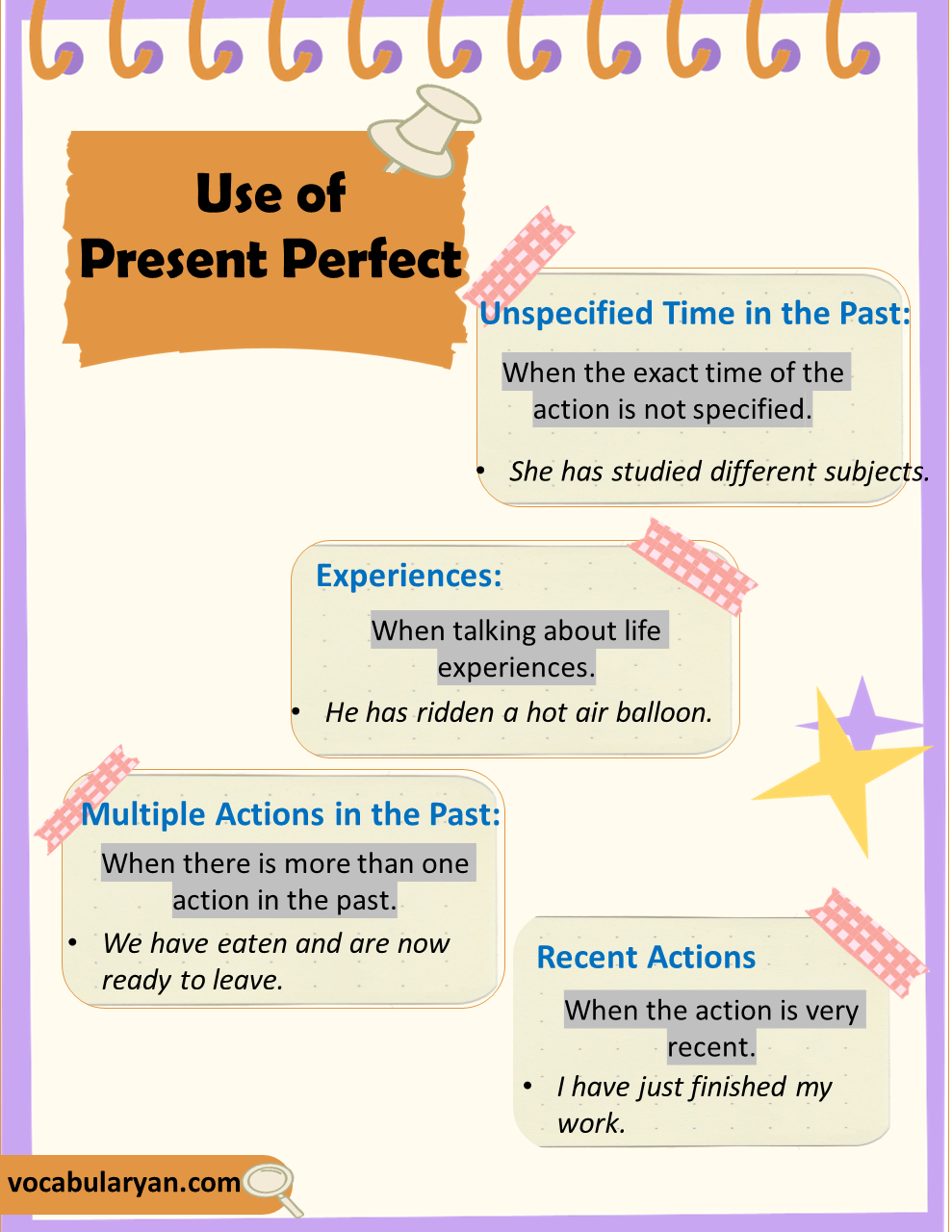
Use of Present Perfect:
1: Unspecified Time in the Past:
When the exact time of the action is not specified.
- I have traveled to many countries.
- She has studied different subjects.
2: Experiences:
When talking about life experiences.
- I have visited the Grand Canyon.
- He has ridden a hot air balloon.
3: Multiple Actions in the Past:
When there is more than one action in the past.
- They have worked hard and achieved success.
- We have eaten and are now ready to leave.
4: Recent Actions:
When the action is very recent.
- I have just finished my work.
- She has recently bought a new car.
Key Features:
- Unspecified Time:
The present perfect tense is used when the exact time of the action is not specified. It focuses on the result or completion of the action rather than when it occurred.
- Connection to the Present:
This tense emphasizes the connection between a past action and the current moment. It is often used to discuss experiences, achievements, or changes that have an impact on the present.
- Auxiliary Verb “Have”:
The choice of “have” or “has” depends on the subject of the sentence. “Have” is used with plural subjects (I, you, we, they), and “has” is used with singular subjects (he, she, it).
Common Mistakes:
- Confusing with Past Simple:
The present perfect is often confused with the past simple tense. Remember that the present perfect indicates a connection between past and present, while the past simply refers to a specific point in the past.
- Incorrect Use of Time Expressions:
Be careful with time expressions. Use “since” with a specific point in time and “for” with a duration.
Examples of Sentences Present Perfect tense:
- I have traveled to five different countries.
- She has graduated with honors.
- We have completed the renovation of our house.
- They have met some famous actors.
- He has written three novels.
- The team has won the championship three times.
- She has bought a new car.
- I have finished reading the book.
- We have lived in this city for ten years.
- The company has introduced innovative products.
- He has visited the Grand Canyon.
- They have learned a new language.
- She has cooked a delicious meal.
- I have received positive feedback.
- We have attended several concerts.
- The project has been completed successfully.
- He has achieved his fitness goals.
- They have explored different hiking trails.
- She has earned a master’s degree.
- We have celebrated our anniversary.
Present Perfect Worksheet
Exercise: Fill in the blanks with the correct form of the present perfect tense of the verbs in parentheses.
- We __________ (never/visit) that museum.
- She __________ (just/arrive) from her trip.
- They __________ (not/start) their homework yet.
- He __________ (travel) to several countries.
- I __________ (eat) at that restaurant before.
- The team __________ (win) many games this season.
- Mary __________ (read) three books this month.
- We __________ (not/see) that movie.
- It __________ (rain) since yesterday.
- John __________ (not/finish) his work.
- She __________ (visit) several countries.
- We __________ (not/eat) at that restaurant before.
- __________ they ever __________ (try) sushi?
- I __________ (read) three books this month.
- By the time we arrived, they __________ (already/leave).
Answers:
- We have never visited that museum.
- She has just arrived from her trip.
- They have not started their homework yet.
- He has traveled to several countries.
- I have eaten at that restaurant before.
- The team has won many games this season.
- Mary has read three books this month.
- We have not seen that movie.
- It has been raining since yesterday.
- John has not finished his work.
- She has visited several countries.
- We haven’t eaten at that restaurant before.
- Have they ever tried sushi?
- I have read three books this month.
- By the time we arrived, they had already left.
You May Also Like






Leave a Comment