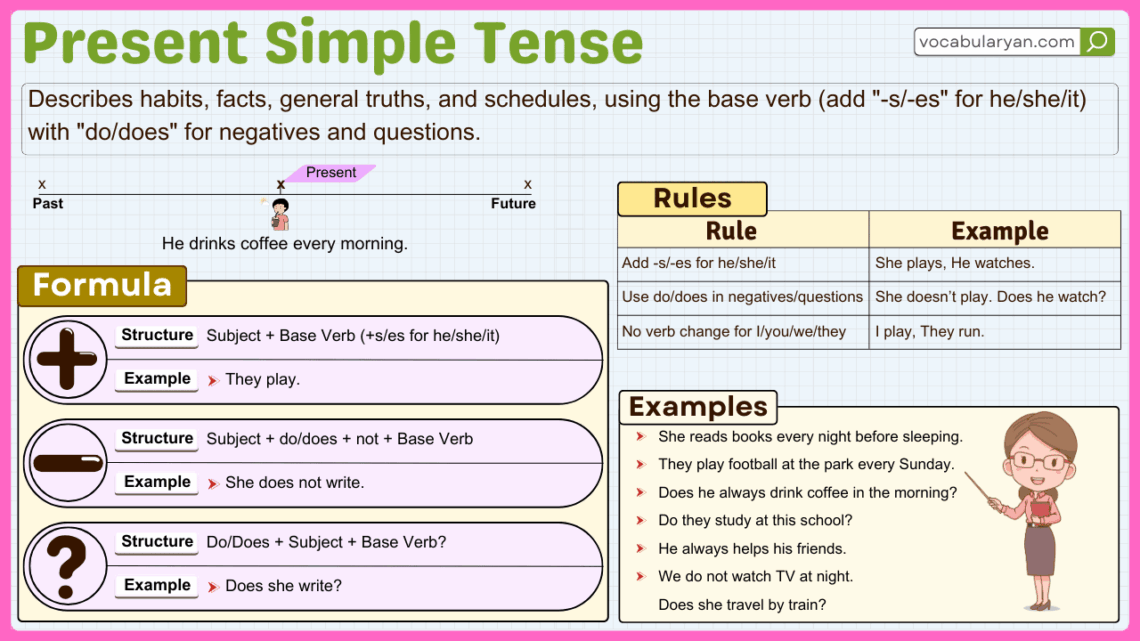
Learning the Present Simple tense is essential for expressing habits, facts, and routines in English. It describes actions that happen regularly or truths that are always valid, such as “She walks to school” or “Water boils at 100°C.” The structure uses the base verb for most subjects, but adds -s or -es for third-person singular (he, she, it). Understanding the Present Simple helps you communicate clearly about everyday activities and general facts with confidence and accuracy.
Structure of the Present Simple Tense
Understanding the structure of this tense is important. It follows a straightforward pattern based on the type of sentence.
Affirmative Sentences
Structure: Subject + base verb (for singular, add -s/es to the verb)
Examples:
- Ahmed reads books every day.
- They play football on weekends.
The first sentence uses reads because Ahmed is singular. In the second, play is used with “they,” which is plural.
Negative Sentences
Structure: Subject + do/does not + base verb
Examples:
- Fatima does not like
- We do not go to school on Sundays.
Does not is used with singular subjects like Fatima, while do not is used with plural subjects like “we.”
Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Do/Does + subject + base verb + ?
Examples:
- Does Ali study at this school?
- Do you enjoy reading novels?
Does begins the question for singular subjects like Ali, while do is used with plural subjects and “you.”
Double Interrogative Sentences
Structure: Wh-word + do/does + subject + base verb + ?
Examples:
- Where does she work?
- Why do they play here?
Here, “where” and “why” ask additional questions before the helping verb.
Subject-Verb Agreement
To use the present simple tense correctly, it’s important to match the subject with the correct verb form.
| Subject | Helping Verb | Example Verb Form |
| I | do | work |
| He/She/It | does | works |
| We/You/They | do | work |
| Ali (singular) | does | works |
| Teachers (plural) | do | work |
| My father | does | works |
| Dogs (plural) | do | bark |
This table correctly reflects the subject-verb agreement, ensuring the verb aligns with singular or plural subjects.
Time Expressions
Time expressions show when the action happens. Here are some common time words used with the present simple tense:
- Every day: I go to school every day.
- Sometimes: She sometimes visits her grandmother.
- Always: Bilal always helps his friends.
- Never: They never miss a meeting.
- On Fridays: We pray at the mosque on Fridays.
Time expressions help clarify when actions occur. For instance, “every day” indicates a regular activity, and “never” shows something does not happen at all.
Adverb Placement
Adverbs like always, often, and never describe how frequently something happens. They usually go before the main verb but after the helping verb.
Examples:
- She always studies in the evening.
- We do not often play video games.
In the first example, always highlights a regular action. The second sentence shows not often reducing the frequency.
Uses of the Present Simple Tense
This tense has several uses. Let’s learn them step by step:
- General Truths: Facts that are always true.
- Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
- The sun rises in the east.
These examples explain universal facts that remain constant over time.
- Habits and Routines: Actions done regularly.
- Aisha reads the Quran every morning.
- They go jogging on Sundays.
The sentences demonstrate regular activities performed consistently.
- Fixed Schedules: Timetables and schedules.
- The train leaves at 9 a.m.
- School starts at 8:30 a.m.
These actions are tied to specific times and do not change.
- Feelings and Emotions: Descriptions of states.
- I like ice cream.
- He loves his family.
Feelings and states describe permanent or long-lasting conditions.
- Instructions or Directions: Steps or guidance.
- You turn left at the next corner.
- Add sugar and stir
Short Answers
Short answers are used to reply briefly to questions in the present simple tense.
| Question | Short Answer |
| Do you like tea? | Yes, I do. |
| Does Sara read books? | No, she does not. |
| Do they play football? | Yes, they do. |
| Does Ahmed study here? | Yes, he does. |
Short answers save time and make responses more direct. They also reflect the tense used in the question.
Question Tags
Question tags are small questions added to the end of a sentence to confirm or clarify information.
| Statement | Question Tag |
| You play cricket, don’t you? | don’t you? |
| She sings beautifully, doesn’t she? | doesn’t she? |
| They don’t eat meat, do they? | do they? |
| He likes sweets, doesn’t he? | doesn’t he? |
Using question tags allows for polite confirmation or checking information.
Examples of the Present Simple Tense
Affirmative
- Ali plays football every evening.
- We visit our grandparents on weekends.
Negative
- Fatima does not eat
- They do not watch
Interrogative
- Does Ahmed like mangoes?
- Do you enjoy swimming?
These examples cover different sentence forms to highlight versatility.
Common Mistakes with the Present Simple Tense
Here are some frequent mistakes and their corrections:
Incorrect verb forms:
- ❌ She go to school every day.
- ✅ She goes to school every day.
Adding “-s” to the verb for singular subjects is essential.
Forgetting the helping verb in negatives:
- ❌ We not like spicy food.
- ✅ We do not like spicy food.
Including do or does ensures grammatical accuracy.
Mixing up singular and plural subjects:
- ❌ Dogs barks at strangers.
- ✅ Dogs bark at strangers.
Matching verbs correctly with singular or plural subjects avoids confusion.
FAQs
What is the structure of the present simple tense? The structure is:
Affirmative: Subject + base verb (+s for singular subjects).
Negative: Subject + do/does not + base verb.
Interrogative: Do/Does + subject + base verb + ?What are common time expressions for present simple tense?
Common time expressions are every day, sometimes, always, never, and on Fridays.
You May Also Like