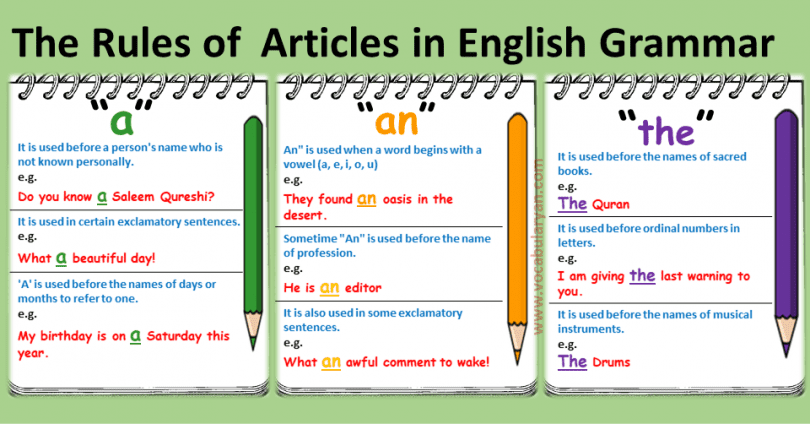
A, an ( indefinite articles) and the (definite article) are the noun makers, noun modifiers, or determiners that appear before the noun or noun equivalents to specify general or specific nouns.
A and An are used before the countable singular non-specific or generic nouns.
The is used before the specific nouns no matter either is singular or plural, countable and uncountable. Although having a robust grip on article usage is one of the most daunting tasks for multilingual writers, it can be your second nature if you practice it thoroughly and precisely. Let’s practice!
There are two kinds of Articles which are following.
(a) Indefinite Article
(b) Definite Article
INDEFINITE ARTICLES
“A” and “An” arc known as Indefinite Articles.
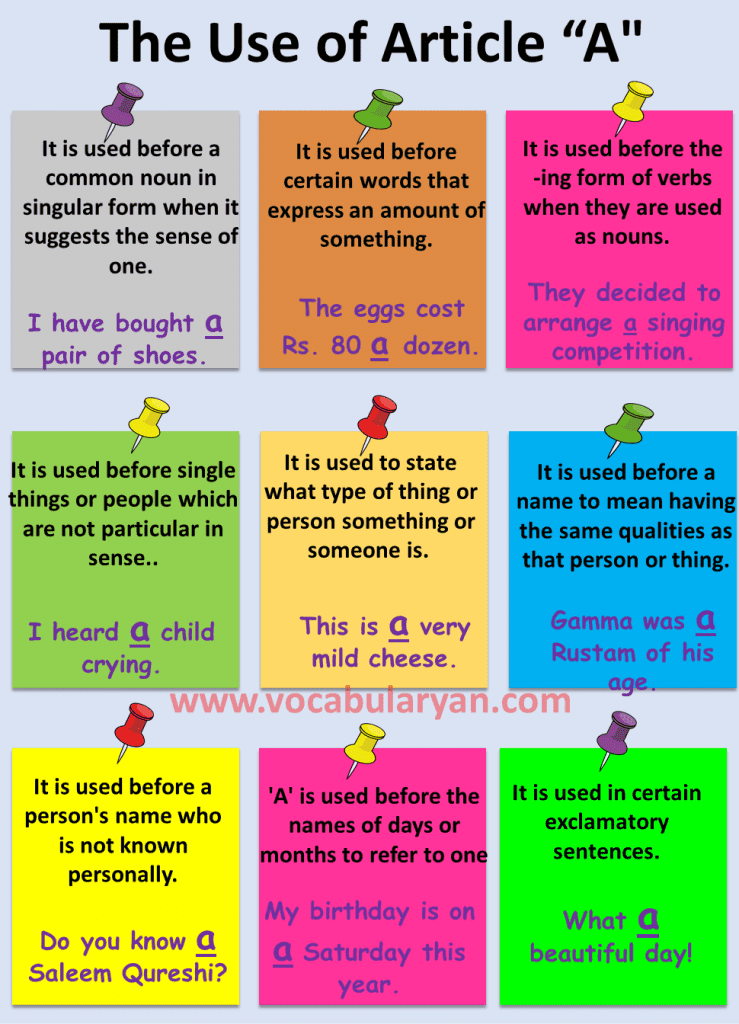
(a) The Use of Article “A”
Examples:
- Do you have a motorbike?
- There is a spider in the bath.
- Twelve inches make a foot.
- I have bought a pair of shoes.
(b) It is used before certain words that express an amount of something.
Examples:
- A few weeks from now I shall be in Lahore.
- I get paid once a month.
- The eggs cost Rs. 80 a dozen.
It is used before a noun to mean all things of that type.
Examples:
- A square has four sides.
- A dog is faithful to its master.
- A cow eats grass.
- A circle has a round shape.
It is used before two nouns that mentioned together so often that they are thought of as one thing.
Examples:
- You should bring a cup and saucer for me.
- Does everyone have a knife and fork?
It is used before singular nouns, especially words for actions, meaning one example of that action.
Examples:
- Take a look at this.
- It needs a good clean.
It is used before the -ing form of verbs when they are used as nouns.
Examples
- The driver paid no attention to a crashing of gears.
- They decided to arrange a singing competition.
- He tried to read writing in French.
- We have learned to read in loud voice.
It is used before an uncountable noun when other information about the noun is added by an adjective or phrase.
Examples:
- Candidates must have a good knowledge of Math.
- She had a beauty that became legendary.
It is used before single things or people which are not particular in sense.
Examples:
- Can I have a banana, please?
- The only furniture in the room was a bed, a table, and two chairs.
- I have got a hole in my shoe.
- There was a sudden loud noise.
- We went to a really good restaurant last night.
- A man stopped me and asked me how to get to the station.
- I heard a child crying.
It is used to state what type of thing or person something or someone is. Examples:
- Is this flower a China rose?
- This is a very mild cheese.
- Experts think that the recently discovered painting may be a Picasso.
It is used before a name to mean having the same qualities as that person or thing.
Examples:
- She may look good on the cinema screen but she will never be a Kate Winslet.
- She was hailed as a new Marilyn Monroe.
- Gamma was a Rustam of his age.
- He is considered to be a Bernard Shaw in Urdu literature.
It is used before a person’s name who is not known personally.
Examples:
- There is a Shazia on the phone for you.
- There is a Mr. Kamran Ahmad to see you.
- Do you know a Saleem Qureshi?
- A certain Mrs. Nadia Irfan wishes to speak to you.
‘A’ is used before the names of days or months to refer to one example.
Example:
- My birthday is on a Saturday this year.
- Well, it is certainly been a June to remember!
It is used in certain exclamatory sentences.
Examples
- What n beautiful day!
- What a silly mistake!
- Bravo! What a wonderful catch.
- Oh! What a terrible storm.
‘A’ is used before consonants and the vowels which arc pronounced as consonants.
Examples:
- I am just going to have a wash.
- Saima is a university student.
- A European teacher came to our college.
- She became frightened of a one-eyed man.
- A kilogram is a unit of mass.
- You saw a boy on a motorbike,
- Saira received a B.A. degree from Karachi University.
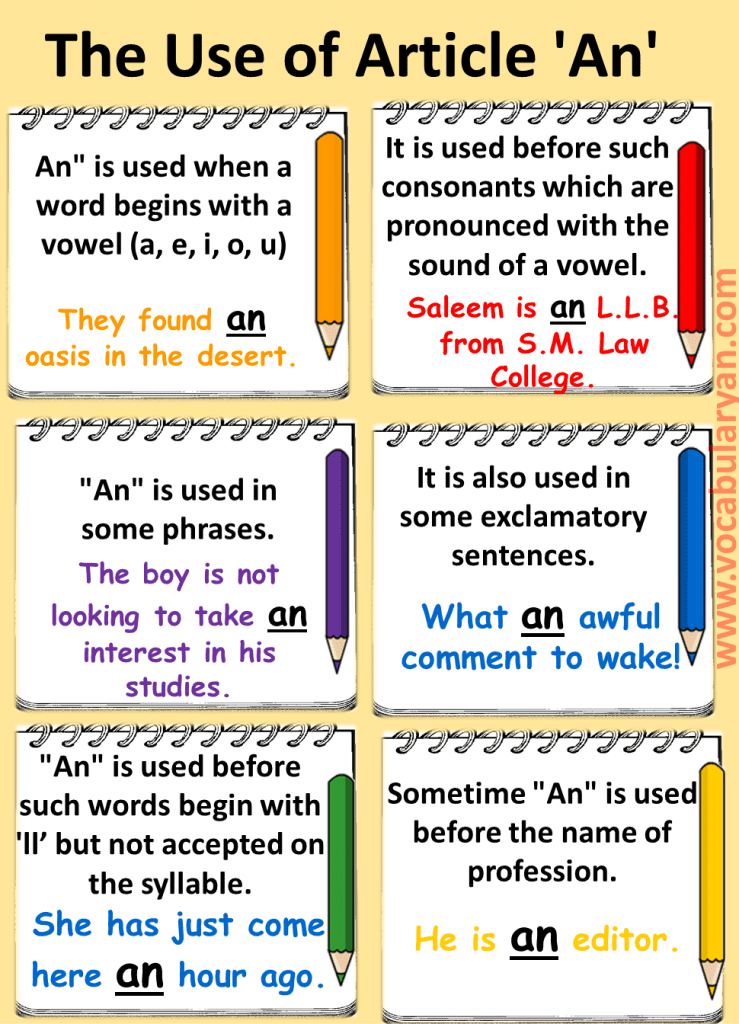
( b) The Use of Article ‘An’
“An” is used when a word begins with a vowel (a, e, i, o, u)
Examples:
- She would like to take on orange.
- An apple a day keeps the doctor away.
- The farmer has bought an ox for plowing.
- An inkpot was placed on the table.
- Draw a neat and labeled diagram of an
- She saw an old man who was working in the field.
- They need an elderly servant in their house.
- She always keeps an umbrella with her.
- You don’t know, he is an idiot boy.
- Grandmother was telling me an interesting story.
- They have made an appalling mistake.
- She has drawn on an ugly face,
- They were playing with an iron ball.
- They found an oasis in the desert.
- It is on the object of measuring time.
It is used before such consonants which are pronounced with the sound of a vowel.
Examples:
- Saleem is an L.L.B. from S.M. Law College.
- He has been elected as art M.P.A from Hyderabad.
“An” is used before such words begin with ‘H’ but not accepted on the syllable.
Examples:
- Abdul Rashid is an honest shopkeeper.
- She has just come here an hour ago.
- Samreen is an heir of her mother’s property.
“An” is used in some phrases.
Examples
- The boy is not looking to take an interest in his studies.
It is also used in some exclamatory sentences.
Examples:
- WoW! What an interesting look.
- What an awful comment to wake!
The” is known as Definite Article.
( C ) The Use of Article “The”
It is used before some nouns that refer to place without showing the exact example of the place.
Examples
- We spent all day at the beach.
- Shall we go to the movies this evening?
- I must go to the bank and change some money.
- You should go to the dentist at least twice a year
It is used before noun phrases in which the range of meaning is limited in some way.
Examples
- I really enjoyed the book I have just finished reading.
- Do you like the other students in our class?
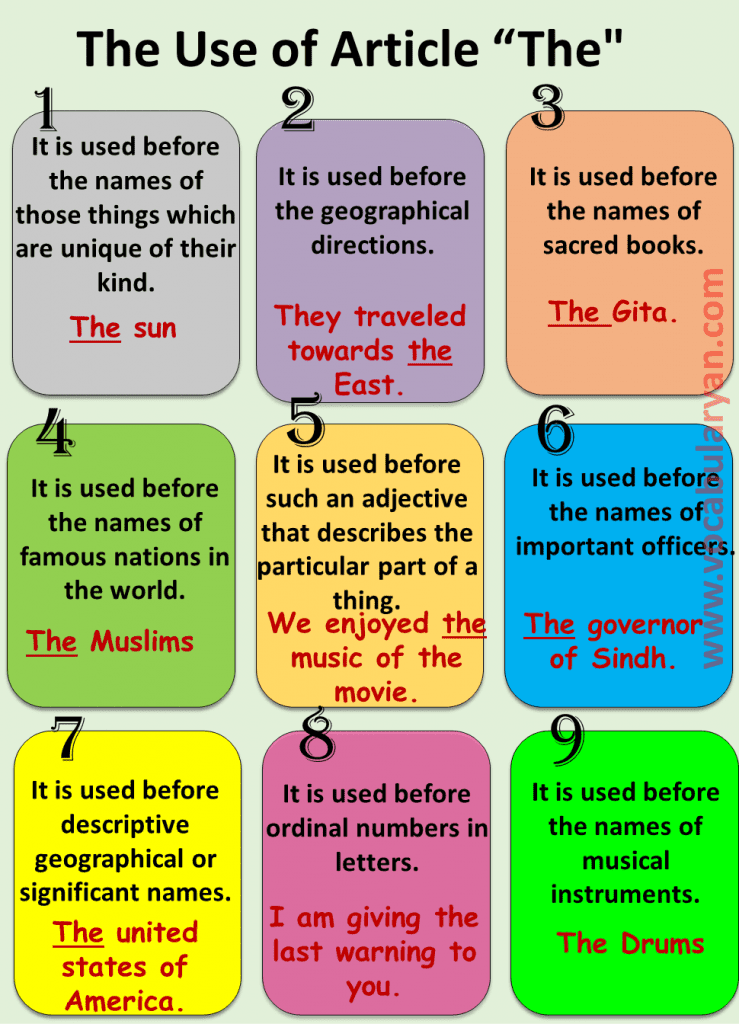
It is used before the names of those things which are unique of their kind.
Examples:
- The sun rises in the east.
- An eagle is flying in the sky.
It is used before the geographical directions.
Examples:
- They traveled towards the
- You should move from here straight towards the
- Children are watching a star in the
- The robbers ran away towards the
It is used before the names of mountains, rivers, oceans, gulfs, and groups of islands.
Examples:
- We have visited the Badshahi Masjid in Lahore.
- The Prime Minister is addressing the National Assembly.
- They would go for justice to the Supreme Court.
- The Senate is the upper house of the Pakistani legislature.
- When we went to Paris, we went up the Eiffel Tower.
It is used ed before the names of famous newspapers, magazines, and journals.
Examples:
- My father reads the Dawn every day.
- I bought the weekly Mag last week.
- The Reader’s digest is famous all over the worm.
- I have read this news in the Indian Times.
It is used when a singular common noun gives a meaning to represent a who e class.
Examples:
- The cat loves comfort.
- The rose is the sweetest of all flowers,
- The dog is a faithful animal.
- The lion is the king of beasts.
It is used when a common noun is used as a substitute for the possessive adjective.
Examples:
- The cows of Mr. Arshad arc beautiful,
- I struck him on the head.
- He stared me in the
- The gold of the nib of the pen is not pure.
- The daughter of your friend walks in that park.
It is used before the names of sacred books.
Examples:
- My mother recites the Holy Quran every day.
- The Gita is written in the form of poetry.
It is used before the names of famous nations in the world.
Examples:
- The French fought hard during the French Revolution.
- The Americans have been distinguished throughout the world.
- The Hindus joined the Indian National Congress in large numbers.
- The Muslims of South Asia had united as a nation.
It is used before such an adjective that describes the particular part of a thing.
Examples:
- He likes the yellow of an egg.
- We enjoyed the music of the movie.
It is used before Proper, Material, and Abstract nouns to make them common.
Examples:
- Swat is the Switzerland of Pakistan.
- The water of Indus is sweet and cold,
- Agha Hashar is the Bernard Shaw of Pakistan.
It is used before the names of important officers.
Examples:
- Begum Rana Liaquat Ali Khan served as the Governor of Sindh.
- The Vice-Chancellor of Karachi University attended the function.
- The President of Pakistan delivered his speech in the last.
It is used before descriptive geographical or significant names.
Examples:
- He decided to go to the United States of America.
It is used before ordinal numbers in letters.
Examples:
- I am giving the last warning to you.
- This was the first experience of her job.
- All of you should read the second chapter carefully.
It is used before the names of musical instruments.
Examples:
- They were beating the drums with high spirit.
It is used before an adjective when it is taken as a noun.
Examples:
- The poor are always worried.
- The rich do not like the poor.
It is used before nouns to indicate a profession.
Examples:
- Asif Jalil has joined the Bar.
- He joined the army as a soldier.
It is used before the superlative degree of an adjective.
Examples:
- Even the darkest cloud has a silver lining.
- She is the most beautiful actress in the play.
It is used before the adverbial comparatives.
Examples:
- The more you earn, the better it is.
- The more they get, the more they want.
It is used sometimes before a noun to give it a force of a superlative.
Examples
- Humaira Arshad is the singer of the
- Shahid Khan Afridi is the man of the match.
- She was the queen of the beauty contest.
- Khalid is the woman of the year.
it is used in certain phrases that express anger or surprise.
Examples
- What the hell are you doing here?
- For the love of God, what will the boy do next?
You May Also Like



Leave a Comment